Barbara Kay: The awkward truth about spousal abuse
One of first-wave feminism’s great achievements in the 1970s was to end the denial surrounding wife abuse in even the “best” homes. Resources for abused women proliferated. Traditional social, judicial and political attitudes toward violence against women were cleansed and reconstructed along feminist-designed lines.
But then a funny thing happened. The closet from which abuse victims were emerging had, everyone assumed, been filled with women. But honest researchers were surprised by the results of their own objective inquiries. They were all finding, independently, that intimate partner violence (IPV) is mostly bidirectional.
But by then the IPV domain was awash in heavily politicized stakeholders. Even peer-reviewed community-based studies providing politically incorrect conclusions were cut off at the pass, their researchers’ names passed over for task force appointments and the writing of training manuals for the judiciary. Neither were internal whistle-blowers suffered gladly. Erin Pizzey, who opened the first refuge for battered women in England in 1971, was “disappeared” from the feminist movement when she revealed what she learned in her own shelter: She committed a heresy by asking women about their own violence, and they told her.
The most extreme IPV is certainly male-on-female, but hard-core batterers and outright killers are rare. In violence of the mild to moderately severe variety that constitutes most of IPV — shoving, slapping, hitting, punching, throwing objects, even stabbing and burning — both genders initiate and cause harm in equal measure.
Every major survey has borne out this truth. In fact, the most reliable, like Canada’s 1999 General Social Survey, found not only that most male and female violence is reciprocal, but also that the younger the sample, the more violent the women relative to men. A meta-analysis of mor than 80 large-scale surveys notes a widening, and concerning, spread — less male and more female IPV — in the dating cohort.
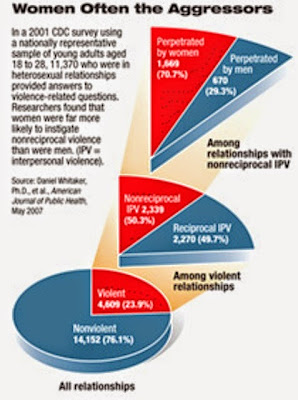
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) has just published its National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey to great fanfare. The survey’s central finding is — yep — that men and women inflict and suffer equal rates of IPV, with 6.5% of men and 6.3% of women experiencing partner aggression in the past year. More men (18%) suffer psychological aggression (humiliation, threats of violence, controllingness) than women (14%). Feminists often define IPV as a “pattern of power and control,” but the survey finds that men were 50% more likely to have experienced coercive control than women (15.2% vs 10.7%).
(While the CDC survey does not reference Canadian data, our IPV statistics vary significantly from the U.S.’s in certain respects. “Minor” wife assault rates as measured on the commonly employed Conflict Tactics Scale are identical, but “severe violence” rates in Canada fall as the violence ratchets up. For “kicking” and “hitting,” Canadian rates were 80% of the American rate; for “beat up,” they were 25%; and for “threatened with or used a gun/knife,” they were only 17%.)
By now there is no excuse for the failure of governments at all levels to follow through on — or at least acknowledge — the settled science of bilateral violence. Yet just last week the Justice Institute of British Columbia issued a lengthy report on “Domestic Violence Prevention and Reduction,” and sure enough, it defines domestic violence as “intimate partner violence against women,” recommending only that government work “to bridge gaps in the services and systems designed to protect women and children.”
In Rethinking Domestic Violence (2006), his third in a series of comprehensive interdisciplinary reviews of IPV and related criminal justice research, University of British Columbia psychology professor Don Dutton cuts through the politicized clutter in this domain. Dutton concludes that personality disorder, culture and a background of family dysfunction, not gender, are the best predictors of partner violence. To further IPV harm reduction, Dutton recommends individual psychological treatment or couples therapy to replace the ideology-inspired thought-reform model, imposed only on male abusers, that has been common (and largely ineffective) practice for many years.
Ironically, and unjustly, abused men today are where women were 60 years ago: their ill-treatment is ignored, trivialized or mocked; there are virtually no funded resources for them; and they are expected to suffer partner violence in silence. Which most of them do.
Who will have the courage to bell this politically correct cat? When will revenge end and fairness begin?
National Post -- Dec 21, 2011 – 7:30 AM ET | Last Updated: Dec 20, 2011 5:35 PM ET
But then a funny thing happened. The closet from which abuse victims were emerging had, everyone assumed, been filled with women. But honest researchers were surprised by the results of their own objective inquiries. They were all finding, independently, that intimate partner violence (IPV) is mostly bidirectional.
But by then the IPV domain was awash in heavily politicized stakeholders. Even peer-reviewed community-based studies providing politically incorrect conclusions were cut off at the pass, their researchers’ names passed over for task force appointments and the writing of training manuals for the judiciary. Neither were internal whistle-blowers suffered gladly. Erin Pizzey, who opened the first refuge for battered women in England in 1971, was “disappeared” from the feminist movement when she revealed what she learned in her own shelter: She committed a heresy by asking women about their own violence, and they told her.
The most extreme IPV is certainly male-on-female, but hard-core batterers and outright killers are rare. In violence of the mild to moderately severe variety that constitutes most of IPV — shoving, slapping, hitting, punching, throwing objects, even stabbing and burning — both genders initiate and cause harm in equal measure.
Every major survey has borne out this truth. In fact, the most reliable, like Canada’s 1999 General Social Survey, found not only that most male and female violence is reciprocal, but also that the younger the sample, the more violent the women relative to men. A meta-analysis of mor than 80 large-scale surveys notes a widening, and concerning, spread — less male and more female IPV — in the dating cohort.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) has just published its National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey to great fanfare. The survey’s central finding is — yep — that men and women inflict and suffer equal rates of IPV, with 6.5% of men and 6.3% of women experiencing partner aggression in the past year. More men (18%) suffer psychological aggression (humiliation, threats of violence, controllingness) than women (14%). Feminists often define IPV as a “pattern of power and control,” but the survey finds that men were 50% more likely to have experienced coercive control than women (15.2% vs 10.7%).
(While the CDC survey does not reference Canadian data, our IPV statistics vary significantly from the U.S.’s in certain respects. “Minor” wife assault rates as measured on the commonly employed Conflict Tactics Scale are identical, but “severe violence” rates in Canada fall as the violence ratchets up. For “kicking” and “hitting,” Canadian rates were 80% of the American rate; for “beat up,” they were 25%; and for “threatened with or used a gun/knife,” they were only 17%.)
By now there is no excuse for the failure of governments at all levels to follow through on — or at least acknowledge — the settled science of bilateral violence. Yet just last week the Justice Institute of British Columbia issued a lengthy report on “Domestic Violence Prevention and Reduction,” and sure enough, it defines domestic violence as “intimate partner violence against women,” recommending only that government work “to bridge gaps in the services and systems designed to protect women and children.”
In Rethinking Domestic Violence (2006), his third in a series of comprehensive interdisciplinary reviews of IPV and related criminal justice research, University of British Columbia psychology professor Don Dutton cuts through the politicized clutter in this domain. Dutton concludes that personality disorder, culture and a background of family dysfunction, not gender, are the best predictors of partner violence. To further IPV harm reduction, Dutton recommends individual psychological treatment or couples therapy to replace the ideology-inspired thought-reform model, imposed only on male abusers, that has been common (and largely ineffective) practice for many years.
Ironically, and unjustly, abused men today are where women were 60 years ago: their ill-treatment is ignored, trivialized or mocked; there are virtually no funded resources for them; and they are expected to suffer partner violence in silence. Which most of them do.
Who will have the courage to bell this politically correct cat? When will revenge end and fairness begin?
National Post -- Dec 21, 2011 – 7:30 AM ET | Last Updated: Dec 20, 2011 5:35 PM ET
IT IS THE CHILD'S HUMAN RIGHT TO ACCESS BOTH PARENTS.
Please view this video it exposes the abuse of both women and men by the family law system. Global action for equal parenting. Take action to expose the trojan horse hidden by the corrupt who seek to abuse the
Child and Family for profit and funding.